| Structural type | C2 |
| Common name | pyrite |
| Definition | |
| Prototype | FeS2 |
| Pearson symbol | cP12 |
| Space group | 205 Pa-3 Th6 |
| Chemical formula | AX2 |
| Bonding | covalent-ionic |
| Atomic positions | A (4a) 0 0 0 (marked by C) |
| Coordination | AX – 6 (deformed 6o), X – X+3A |
| Sublattices | A – fcc |
| PDB files | C2 (in ideal tetrahedral coordination of X) |
| Parameters | 1/3<xi<1/2 |
| Special values | C1 for xi=1/4 (out of range), xi=1/2 – ideal 6o coordination for A and zero XX distance |
| Substances | late transition metal + V or VI element (see the table below), CaC2 |
The boundaries on xi are of the following reasons: xi<1/2 because XX distance must be positive, if xi crosses 1/3 then the coordination of X atom principally changes. The distances to the nearest neighbors are plotted in the figure below, from which it follows that xi is determined by the coordination of X atom.
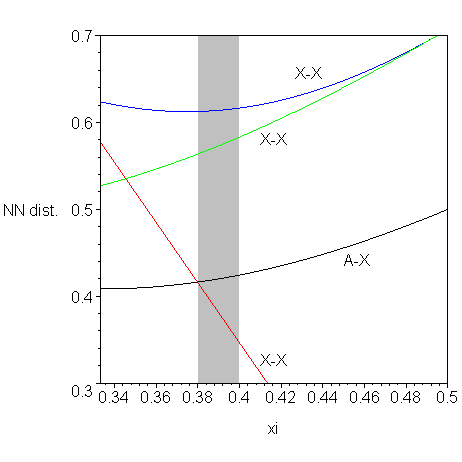
| A | X | a | xi | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn | S | 6.1008 | .4012 | hauerite |
| Fe | S | 5.4067 | .386 | pyrite |
| Co | S | 5.5240 | .389 | cattierite |
| Ni | S | 5.6770 | .395 | vaesite |
| Ru | S | 5.6106 | .3883 | laurite |
| Os | S | 5.6196 | .390 | erlichmanite |
| Fe | Se | 5.783 | .386 | dzharkenite |
| Co | Se | 5.8588 | .380 | trogtalite |
| Ni | Se | 6.000 | .384 | penroseite |
| Cu | Se | 6.056 | .386 | krutaite |
| Pt | P | 5.6956 | .394 | |
| Pt | As | 5.9665 | .383 | sperrylite |
| Pt | Sb | 6.428 | .380 | geversite |
| Pt | Bi | 6.691 | .386 | insizwaite |
| Au | Sb | 6.659 | .386 | aurostibite |