 |  |
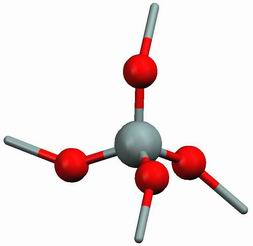
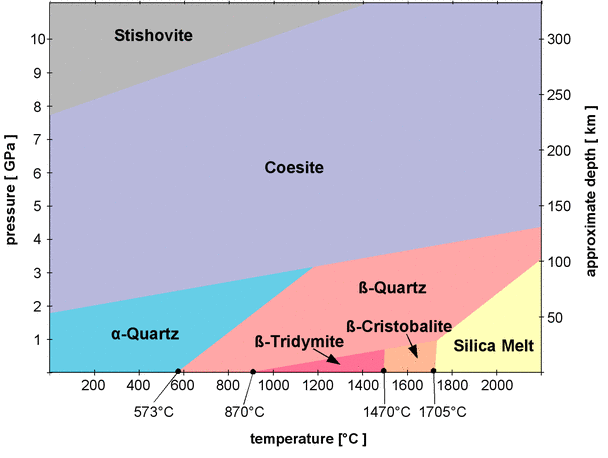
Silica is one of the most abundant substances, it is used widely in microelectronics and optics. The building blocks of silica crystals are SiO4 tetrahedra which combine in different polymorphic forms (the phase diagram is from www.quartzpage.de):
| α-quartz | 3* | 154 | P3221 | enantiomorphic with P3121 |
| β-quartz | 3 | 180 | P6222 | C8, enantiomorphic with P6422 |
| α-crystobalite | 4 | 92 | P41212 | enantiomorphic with P43212 |
| β-crystobalite | 2 | 227 | Fd-3m | C9 (Si with O in bonds), see also cubic (8*, P213) and tetragonal (2, I-42d) distortions |
| α-tridymite | 4 | 20 | C2221 | see also monoclinic (24, Cc) distortion |
| β-tridymite | 3 | 194 | P63/mmc | C10 |
| coesite | 8 | 15 | C2/c | |
| stishovite | 2 | 136 | P42/mnm | C4 |
| α-moganite | 6 | 15 | C2/c | |
| β-moganite | 6 | 72 | Ibam |
* Number of units per primitive cell
Note that α and β forms are respectively low and high temperature forms. Other crystal structures include keatite (12, P41212), high pressure crystobalite (8, P21/c), next to stishovite high pressure polymorph (4, Pa-3). Other forms include lechatelierite (amorphous fused silica), vitreous silica (amorphous silica in glass phase), silica zeolites (example), silica aerogels, and other forms.
Optical bandgap (fundamental absorption edge): 9.0 eV (α-quartz)
Band structure of α-quartz [Gritsenko95,DiPomponio95]:
| 9 eV | delocalized Si s,d and O s electrons |
| 0 ÷ 9 eV | bandgap |
| -4 ÷ 0 eV | O 2p2 nonbonding electrons, perpendicular to O–Si–O plane |
| -10 ÷ -4 eV | Si 3sp3 and O 2p2 bonding electrons, extend to 0 eV |
| -20 eV | O 2s2 core electrons |
Oxygen deficient centers (ODC):
| neutral oxygen vacancy (NOV) or ODC(I) | ≡Si–Si≡ | 2.68 Å vs. 2.35 Å in bulk Si, [Mukhopadhyay05b] |
| paramagnetic E' center | ≡Si· | |
| E'γ, positively charged puckered (back projected) oxygen vacancy | ≡Si–Si≡ + h → ≡Si++ ·Si≡ | [Buscarino06,Mukhopadhyay05a] |
| E'δ (??), dimer configuration E' center | ≡Si–Si≡ + h → ≡Si·Si≡ | [Mukhopadhyay05a] |
| twofold-coordinated Si or ODC(II) (hole center) | =Si: |
Oxygen related centers:
| nonbridging oxygen (NBO) or nonbridging oxygen hole center (NBOHC) | ≡Si–O· | [Suzuki03] |
| peroxy radical (POR) | ≡Si–O–O· | |
| peroxy linkage (POL) | ≡Si–O–O–Si≡ |
Excitons are self-trapped (STE) in the following configuration: has its electronic component in (≡Si·) and hole component in (≡Si–O·) [Ismail-Beigi05].
Absorption bands inside bandgap (decomposed):
| E,eV | FWHM,eV | osc.strength | center | |
| 2.0 | 0.5 | 1.5×10-4 | NBO | [Cannas06,Bakos04] |
| 4.8 | 1.0 | 0.03 | NBO | [Cannas06,Bakos04,Cannas04] |
| 5-6 | ≡Si· | [Mukhopadhyay05a] | ||
| 7.6 | NOV | [Mukhopadhyay05b,Agnello03,Cannas04] |
Emission bands (decomposed):
| band | E,eV | FWHM | t | center | |
| 1.9 | 0.1-0.2 | 8-15 µs | NBOHC | [Cannas06,Bakos04,Glinka02] | |
| γ | 2.7-2.8 | 0.7 | 5-10 µs | NOV(Tσ*→σ) | [Glinka02,Meinardi98] |
| β | 3.1-3.2 | 0.4 | STE | [Cannas02,Meinardi98] | |
| α | 4.2-4.4 | 0.5 | 4-10 ns | STE,ODC(II) | double structure, [Cannas02,Meinardi98,Agnello03] |
Surface's NBOHC has 1.8 eV and decay times up to 1 ms. Lifetimes are typically grow up with disorder [Glinka02].